Hydropneumatic suspension simulation of a 4x4 car for "GIDRO-STAR" LLC
Simulation object: hydropneumatic suspension of a 4x4 car with diagonal hydraulic connections of the hydropneumatic compressor cavities (HPC).
Simulation objective: obtain static and dynamic characteristics of the suspension (HPC) in the presence of external disturbances on the HPC rods.
Simulation tasks:
- obtain the elastic-damping characteristic of a single HPC;
- obtain the elastic-damping characteristics of two HPC having hydraulic connections;
- obtain the elastic-damping characteristics of the HPC in the presence of hydraulic and kinematic connections of the HPC.
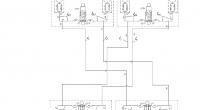
The basic hydraulic scheme of the hydropneumatic suspension of the car (without control devices) is shown in the figure to the right of the text.
The work was performed in the ESI SimulationX software, which allows creating a model of a hydropneumatic spring, taking into account:
- its main design and operating parameters;
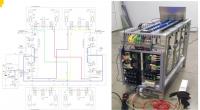
- hydraulic connections with other springs (fig. 3);
- kinematic connections with other springs (fig. 4);
- lengths of hydraulic lines, hydraulic resistances of dampers;
- elasticity of the high-pressure hoses;
- friction in the sliding pairs of the hydraulic cylinder and the hydraulic pneumatic accumulator;
- thermodynamic processes occurring in the working fluid and gas;
- spring loading conditions.
The simulation results of the hydropneumatic compressor loading were presented in graphical dependences of the changes in the operating parameters of hydraulic cylinders and hydropneumatic accumulators over time. The dependence of the force on the hydraulic cylinder rod and the movement of the hydraulic cylinder rod on time were analyzed.
This project was a replacement for a series of bench tests of various suspension options to save resources for conducting field experiments and determining the operating parameters of the suspension elements. With the help of SimulationX software, Nova-Engineering specialists replaced traditional analytical calculations (very time-consuming) and achieved the required elastic-damping characteristics of the suspension, taking into account the hydraulic and kinematic connections of the HPC
- commented
leading engineer of Hydro-star company,
M. Yu. Karpushkin
The basic hydraulic scheme of the hydropneumatic suspension of the car (without control devices) is shown in Fig. 1.
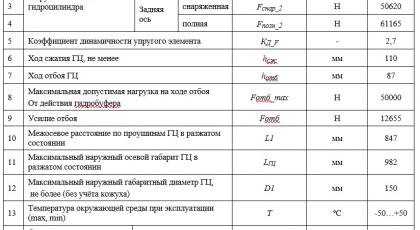
The primary parameters of the suspension elements are presented in Table 1.

Figure 1 – hydraulic diagram of the hydropneumatic suspension system
Drive axles with hydropneumatic suspension
Rear steerable axle with longitudinal hydraulic cylinders


Figure 4 – Model of hydropneumatic springs with hydraulic and kinematic connections
Figure 5 – HPC model with sinusoidal loading

The results of modeling the loading of hydropneumatic springs can be represented by graphical dependences of changes in the operating parameters of hydraulic cylinders and hydropneumatic accumulators over time. Figure 6 shows the dependence of the change in the force on the hydraulic cylinder rod and the movement of the hydraulic cylinder rod on time.
Figure 3 – Model of hydropneumatic springs with hydraulic communication of cavities and with step loading of one HPC